Understanding the Risks of Using Carbon Steel Strike Anchors in High-Temperature or Humid Environments
2025-05-25
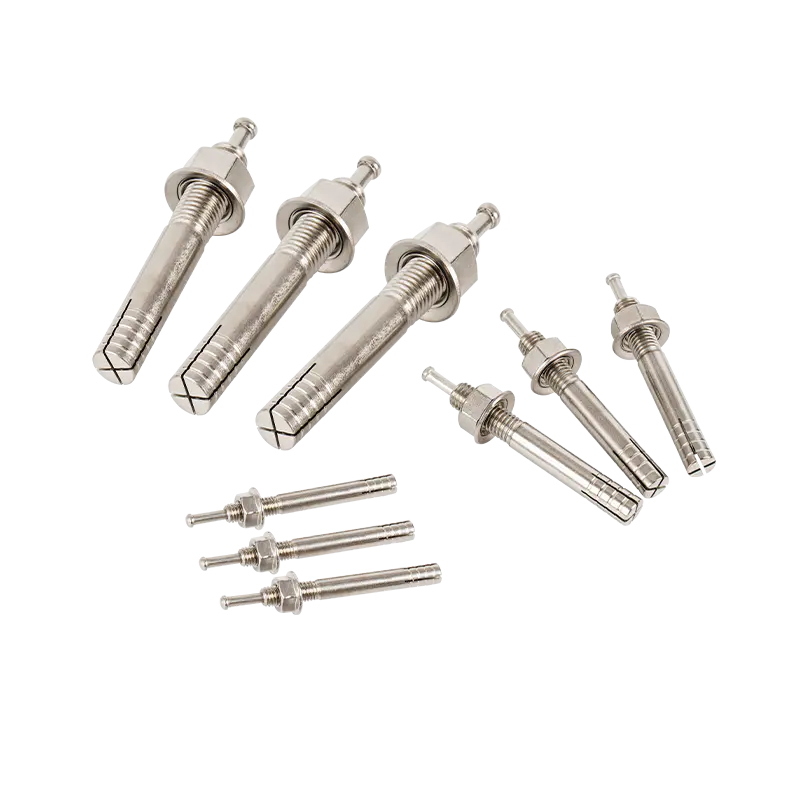
In construction and engineering, Carbon Steel Strike Anchors are widely valued for their robust load-bearing capacity and reliability in securing heavy fixtures to concrete and masonry. However, professionals must critically assess their application in extreme environmental conditions, particularly high-temperature or humid settings, where inherent material vulnerabilities could compromise performance and safety.
Thermal Stress and Structural Integrity
Carbon steel’s mechanical properties are temperature-sensitive. Prolonged exposure to temperatures exceeding 400°F (204°C) risks annealing—a process where the metal softens due to heat-induced microstructural changes. For Carbon Steel Strike Anchors, this can reduce tensile strength and load capacity, potentially leading to anchor slippage or failure under stress.
Additionally, cyclic thermal expansion and contraction in high-heat environments may weaken the bond between the anchor and substrate. Over time, this creates micro-fractures in the surrounding concrete, diminishing the anchor’s holding power. Engineers working in industries like metallurgy or energy, where high temperatures are common, should consider heat-resistant alternatives such as stainless steel or specialized alloys.
Corrosion Risks in Humid or Wet Conditions
Carbon steel’s susceptibility to oxidation is a well-documented limitation. In humid or coastal environments, moisture accelerates corrosion, forming rust that erodes the anchor’s cross-sectional area and weakens its mechanical integrity. Chloride-rich atmospheres—common near seawater or de-icing chemicals—exacerbate pitting corrosion, creating localized weak points that may escape visual inspection until failure occurs.
Corroded Carbon Steel Strike Anchors risk catastrophic failure in dynamic load scenarios, such as seismic activity or vibration-heavy machinery. Even in static applications, gradual corrosion can undermine long-term reliability, necessitating frequent inspections and replacements that drive up lifecycle costs.
Mitigation Strategies for Safe Use
To address these risks, industry experts recommend proactive measures:
Protective Coatings: Galvanization or epoxy coatings can shield Carbon Steel Strike Anchors from moisture. However, coatings must remain intact during installation; scratches or abrasions expose bare metal to corrosion.
Material Substitution: In permanently humid or high-temperature settings, stainless steel (e.g., Grade 316) or hot-dip galvanized anchors offer superior resistance.
Environmental Monitoring: Regularly assess temperature fluctuations and humidity levels. Implement drainage or ventilation systems to reduce moisture exposure.
Routine Inspections: Schedule non-destructive testing (e.g., ultrasonic thickness measurements) to detect early signs of corrosion or deformation.
While Carbon Steel Strike Anchors remain a cost-effective solution for many applications, their limitations in extreme environments demand careful risk assessment. Engineers and contractors must prioritize environmental compatibility during material selection, balancing upfront costs against long-term safety and durability. As industry standards evolve, adopting corrosion-resistant materials and advanced monitoring techniques will be critical to mitigating failure risks and ensuring structural resilience.

 English
English 日本語
日本語